使用Lybic的Gradio Playground示例
该页面展示了如何在Gradio Playground中使用Lybic
此文档提供了一步步的教程,指导您构建一个能够理解并在计算机上执行复杂任务的图形用户界面 (GUI) 智能体。
在此文档中,我们将使用双模型架构实现电脑端使用:一个用于高级规划,另一个用于落地执行(Grounding)操作。
高级规划模型使用最先进的规划模型(例如 OpenAPI O3 和 Gemini 2.5 Pro),而视觉基础操作则使用专为桌面任务优化的 doubao-UITARS 模型。
我们将演示如何结合使用 LangChain、Gradio 和 Gemini、doubao-uitars 模型,创建一个能够在 LybicSDK 提供的安全沙盒桌面环境中查看屏幕、思考并执行操作的 AI智能体。
当然,您也可以通过引用其他模型依赖,轻松将 Gemini 模型替换为其他多模态模型。
1. 初始化Python项目并安装依赖项
首先,确保您已经安装了Python 3.10或更高版本。然后,您可以使用以下命令初始化一个新的Python项目并安装所需的依赖项:
mkdir gradio-playground
cd gradio-playground
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # 在Linux或macOS上
venv\Scripts\activate # 在Windows上
pip install -U pip
pip install -U python-dotenv langchain-core langchain-google-genai langchain-openai langchain gradio lybic2. 设置环境变量
从 Google-Ai-Studio 获取您的API密钥,并将其添加到项目根目录中的 .env 文件中, 填充环境变量GOOGLE_API_KEY:
GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_google_api_key_here获取火山方舟API密钥 ,并将其添加到 .env 文件中, 使环境变量ARK_API_KEY充满, 并配置端点和接地模型:
ARK_API_KEY=your_api_key
ARK_MODEL_ENDPOINT=https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3
ARK_MODEL_NAME=doubao-1-5-ui-tars-2504283. 编写一个简易的Gradio Playground,让智能体能够在Gradio界面中与用户对话
import os
import dotenv
dotenv.load_dotenv(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), ".env"))
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_core.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
import gradio as gr
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-2.5-flash", temperature=0.7)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["history", "user_input"],
template="You are a helpful assistant. Below is the conversation history:\n{history}\n\nUser input: {user_input}\n\nAssistant response:"
)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="history")
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt, memory=memory)
def playground(user_input, history=None):
if not user_input or user_input.strip() == "":
return "It looks like you didn't provide any text for me to respond to! Please type or paste your input, and I'll be happy to help.", history or []
try:
response = chain.invoke({"user_input": user_input})["text"]
new_history = history + [[user_input, response]] if history else [[user_input, response]]
return "", new_history
except Exception as e:
return f"Error: {str(e)}", history
with gr.Blocks() as iface:
gr.Markdown("# Playground with LangChain & Gradio")
gr.Markdown("Interact with the Gemini model and maintain conversation history.")
chatbot = gr.Chatbot()
user_input = gr.Textbox(placeholder="Enter your question or prompt here...")
submit_button = gr.Button("Submit")
submit_button.click(
fn=playground,
inputs=[user_input, chatbot],
outputs=[user_input, chatbot],
)
user_input.submit(
fn=playground,
inputs=[user_input, chatbot],
outputs=[user_input, chatbot],
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
iface.launch()将上述代码保存为 app.py 文件, 并在终端中运行以下命令启动Gradio应用:
python app.py打开浏览器并访问 http://127.0.0.1:7860,您将看到一个简单的Gradio界面,您可以在其中与Gemini模型进行对话。
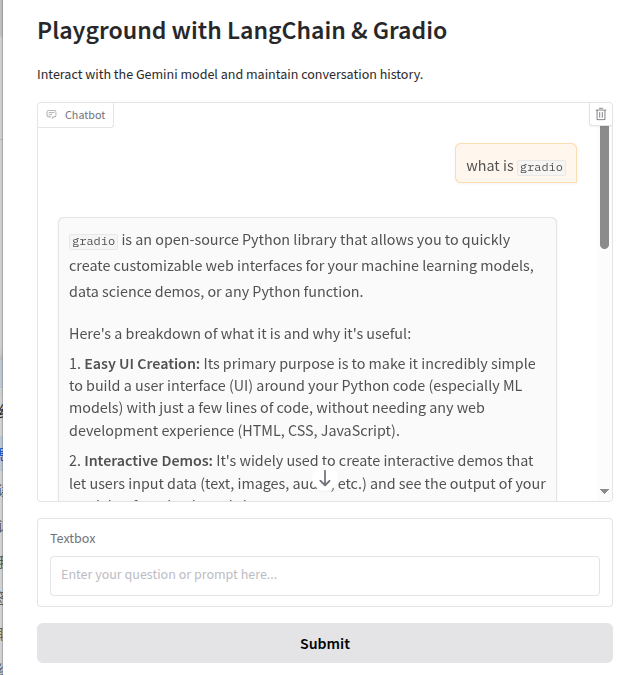
4. 将lybic集成到你的Gradio Playground中
在你的脚本中,导入 lybic 并通过调用 LybicClient() 进行初始化。
from lybic import LybicClient
async def main():
# you should set env vars before initialize LybicClient
async with LybicClient() as client:
pass从沙盒环境中获取屏幕截图。
import asyncio
from lybic import LybicClient, Sandbox
async def main():
async with LybicClient() as client:
sandbox = Sandbox(client)
url, image, b64_str = await sandbox.get_screenshot(sandbox_id="SBX-xxxx")
print(f"Screenshot URL: {url}")
image.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
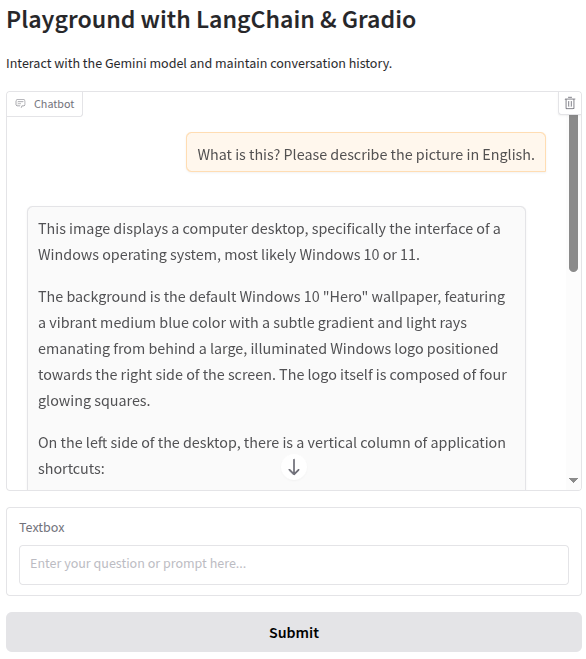
asyncio.run(main())修改消息输入:导入 langchain_core.messages 模块,并将之前的单条消息转换为结构化的消息列表,以支持多种消息类型。
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, AIMessage, HumanMessage
messages = [
HumanMessage(
content=[
{
"type": "text",
"text": "What is this? Please describe the picture in English."
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": f"data:image/webp;base64,{ b64_str }"
}
}
]
),
]
5. 构建双智能体处理循环
0. 介绍
这是模块中最关键的部分。
该智能体程序的架构实际上非常简单,其执行流程如下:
- 用户输入命令:例如,“帮我预订下周二下午 3 点左右从洛杉矶飞往亚特兰大的航班,并在 booking.com 上预订亚特兰大机场附近的酒店房间。”
- 智能体通过Lybic SDK 从沙盒环境中捕获屏幕截图。
- 进入循环:将屏幕截图、用户命令和系统提示(以及上一步的全局上下文和内存)发送给大型语言模型 (LLM),以便 LLM 制定总体(或下一步)计划。
- LLM 生成总体计划,例如“我现在在桌面上。我需要打开浏览器,访问 booking.com,然后选择预订……”
- 高级计划存储为全局上下文和记忆,并在后续每次请求时作为附加的“总体计划”传递。
- 分解计划并执行:例如,“打开浏览器 -> 获取浏览器的桌面坐标。”
- 生成具体的动作命令。
- 将动作指令传递给 Lybic SDK 执行。
- 返回步骤 3,直到 LLM 判断任务完成并退出循环。
我们需要确保流程中非循环部分能够成功运行并符合预期,然后再在主流程的末尾添加循环。
好的,让我们修改上一步的代码。
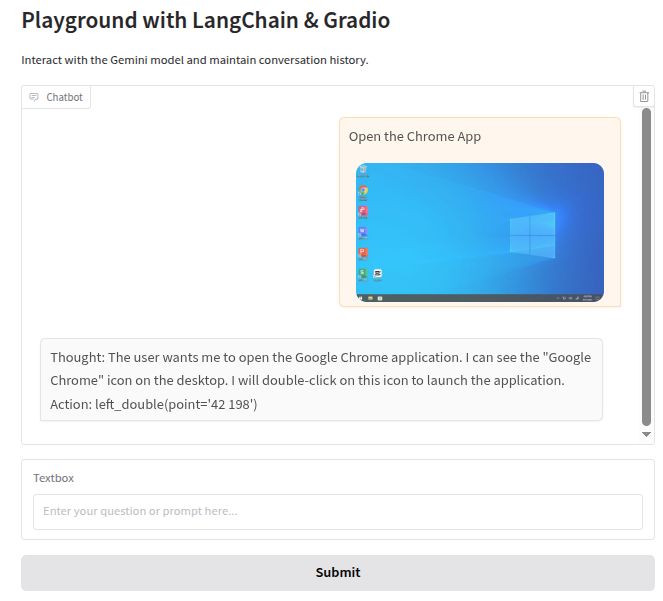
1. 查看截图
我们可以在聊天框中查看每个步骤的截图,查看截图非常简单。
我们只需要启用 Gradio 的 Markdown 文本渲染功能,然后以 Markdown 格式输出图像消息即可。
在 chatbot = gr.Chatbot() 这一行,添加 render_markdown=True,如下所示:chatbot = gr.Chatbot(render_markdown=True)
然后,从沙盒获取截图 URL:screenshot_url, _, base64_str = await sandbox.get_screenshot('sandbox_id')
将截图 URL 添加到 Markdown 文本中:user_message_for_history = f"{user_input}\n\n"
2. 为Gemini规划模型设置系统提示词
You are a GUI Planner agent. You need to perform the next action to complete the task.
You have a access to a sandbox environment which are running Windows OS. You should ensure your action follows Windows common sense, such as double click to open a software on desktop, or use right click for context menu, and so on.
You should describe the next ONE action in English, such as:
- double click at "Google Chrome" icon
- right click at "This PC" icon
- click the close button at the top right corner
- press Alt+F4
- type "terms"
- wait 5 seconds
After that, an agent will execute the action you describe, and a new screenshot will be attached, you can use it to plan the next step.3. 为doubao-uitars模型设置系统提示词
You are a GUI Grounding Agent, proficient in the operation of various commonly used software on Windows, Linux, and other operating systems.
Please complete the GUI Planner Agent's task based on its input, history Action, and screenshots.
The user(GUI Planner Agent) will input a current screenshot and a text including `ActionSummary` and `Action`.
You need to analyze and process `ActionSummary` and `Action` from GUI Planner Agent, and output only one Action at a time, please strictly follow the format below.
## Output Format
Thought: ...
Action: ...
## Action Space
click(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
left_double(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
right_single(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
drag(start_point='<point>x1 y1</point>', end_point='<point>x2 y2</point>')
hotkey(key='ctrl c') # Split keys with a space and use lowercase. Also, do not use more than 3 keys in one hotkey action.
type(content='xxx') # Use escape characters \', \", and \n in content part to ensure we can parse the content in normal python string format. If you want to submit your input, use \n at the end of content, and next action use hotkey(key='enter')
scroll(point='<point>x1 y1</point>', direction='down or up or right or left') # Show more information on the `direction` side.
wait() #Sleep for 5s and take a screenshot to check for any changes.
finished(content='xxx') # Use escape characters \', \", and \n in content part to ensure we can parse the content in normal python string format.
## Note
- Use English in `Thought` part.
- The x1,x2 and y1,y2 are the coordinates of the element.
- The resolution of the screenshot is 1280*720.
- Write a small plan and finally summarize your next action (with its target element) in one sentence in `Thought` part.4. 将系统提示词添加到消息列表中
在 full_message_list = history_messages + message 这一行之前添加 system_message = SystemMessage(content=SYSTEM_PROMPT),
并将 full_message_list = history_messages + message 修改为 full_message_list = [system_message] + history_messages + message。
如果一切正常,当你像这样测试输入和输出时,LLM 不会输出正确的坐标格式:
Thought: 用户想要打开 Google Chrome 应用程序。我可以在桌面上看到“Google Chrome”图标。我需要双击此图标来启动应用程序。 Action: left_double(point='')
这是因为 Gradio 的默认行为是清理 HTML 以防止潜在的安全问题,但这可能会干扰你想要渲染特定 HTML 标签。
我们只需要调整 gr.Chatbot 组件以禁用 HTML 清理功能。
在 chatbot = gr.Chatbot(render_markdown=True) 这一行,将 sanitize_html=False 添加到 gr.Chatbot 组件中,如下所示:chatbot = gr.Chatbot(render_markdown=True, sanitize_html=False)
好的,让我们测试一下系统提示是否有效。
5. 引入uitars模型
Ui-tars 是一种可以识别屏幕坐标和用户交互的模型,但它目前在 LangChain 中尚不可用。
不过,好消息是:Ui-tars 的请求接口符合 OpenAI API 规范,因此我们可以自行开发一个 Ui-tars 客户端。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm_uitars = ChatOpenAI(
base_url=os.getenv("ARK_MODEL_ENDPOINT"),
api_key=os.getenv("ARK_API_KEY"),
model=os.getenv("ARK_MODEL_NAME"),
)6. 使用 Lybic API 解析大型语言模型的输出并执行相应动作。
Lybic 提供了一个简单的 API,可以通过 ComputerUse().parse_llm_output() 解析大型语言模型 (LLM) 的输出并执行相应的操作。
阅读此文档了解更多信息。
为了测试执行结果,我们添加了一个新功能:查看执行结果。 此功能会在执行完成后弹出一个图片供我们查看。
_, img, _ = await sandbox.get_screenshot(sandbox_id);img.show()
好的,让我们测试一下执行结果。
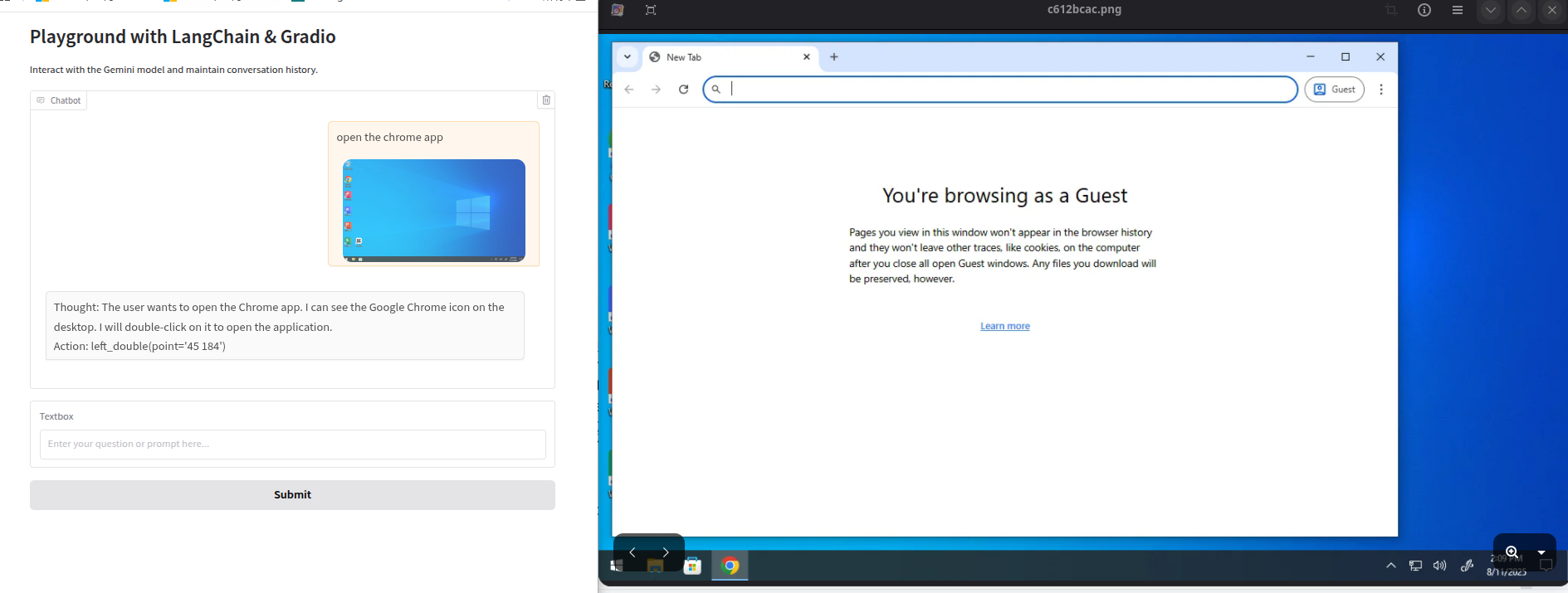
执行结果正确。
7. 引入事件-问题求解循环
在这一步,我们将引入一个事件-问题求解循环,用于解决大型语言模型(LLM)无法一次性完成的复杂任务。
LLM 需要将大型任务分解成多个小任务,逐一执行,并在每一步判断“是否已完成任务或需要规划下一步”。
为了使 LLM 能够像智能体一样在循环中处理任务,我们需要修改 playground 函数,使其能够持续循环执行“观察-思考-行动”过程,直到任务完成。
这需要进行以下修改:
- 引入主循环:在 playground 函数中,我们将添加一个 while 循环来模拟智能体的持续工作。
- 状态跟踪:循环中的每一步都需要获取最新的屏幕截图作为智能体的“观察”输入。
- 终止条件:智能体需要知道任务何时完成。我们将依靠 LLM 输出的 finished() 动作作为循环退出信号。
- 实时反馈:为了让用户看到智能体执行的每一步,我们将利用 Gradio 在循环的每一步更新聊天记录。
- 重要 使用
yield使函数异步返回。 - 重要 在
history.append([user_message_for_history, "Thinking..."])之后添加while True循环。 - 使用 LLM 的思考过程更新历史记录:
history[-1][1] = response - 检查终止条件:
if isinstance(action, dto.FinishedAction):
8. 完整代码
import asyncio
import os
import dotenv
import re
dotenv.load_dotenv(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), ".env"))
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from lybic import LybicClient, Sandbox, ComputerUse, dto
import gradio as gr
PLANNER_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a GUI Planner agent. You need to perform the next action to complete the task.
You have a access to a sandbox environment which are running Windows OS. You should ensure your action follows Windows common sense, such as double click to open a software on desktop, or use right click for context menu, and so on.
You should describe the next ONE action in English, such as:
- double click at "Google Chrome" icon
- right click at "This PC" icon
- click the close button at the top right corner
- press Alt+F4
- type "terms"
- wait 5 seconds
After that, an agent will execute the action you describe, and a new screenshot will be attached, you can use it to plan the next step.
"""
GROUNDNING_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are a GUI Grounding Agent, proficient in the operation of various commonly used software on Windows, Linux, and other operating systems.
Please complete the GUI Planner Agent's task based on its input, and screenshots.
The user(GUI Planner Agent) will input a current screenshot and an actio text.
You need to analyze and process `action` from GUI Planner Agent, and output only one Action at a time, please strictly follow the format below.
## Output Format
Thought: ...
Action: ...
## Action Space
click(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
left_double(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
right_single(point='<point>x1 y1</point>')
drag(start_point='<point>x1 y1</point>', end_point='<point>x2 y2</point>')
hotkey(key='ctrl c') # Split keys with a space and use lowercase. Also, do not use more than 3 keys in one hotkey action.
type(content='xxx') # Use escape characters \', \", and \n in content part to ensure we can parse the content in normal python string format. If you want to submit your input, use \n at the end of content
scroll(point='<point>x1 y1</point>', direction='down or up or right or left') # Show more information on the `direction` side.
wait() #Sleep for 5s and take a screenshot to check for any changes.
finished(content='xxx') # Use escape characters \', \", and \n in content part to ensure we can parse the content in normal python string format.
## Note
- Use English in `Thought` part.
- The x1,x2 and y1,y2 are the coordinates of the element.
- The resolution of the screenshot is 1280*720.
- Write a small plan and finally summarize your next action (with its target element) in one sentence in `Thought` part.
"""
sandbox_id = os.getenv("SANDBOX")
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(model="gemini-2.5-flash", temperature=0.7)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="history")
llm_uitars = ChatOpenAI(
base_url=os.getenv("ARK_MODEL_ENDPOINT"),
api_key=os.getenv("ARK_API_KEY"),
model=os.getenv("ARK_MODEL_NAME"),
)
async def playground(user_input, history=None):
if not user_input or user_input.strip() == "":
yield (
"It looks like you didn't provide any text for me to respond to! Please type or paste your input, and I'll be happy to help.",
history or [],
)
return
if history is None:
history = []
try:
async with LybicClient() as client:
sandbox = Sandbox(client)
computer_use = ComputerUse(client)
# Add the initial user input to the history
screenshot_url, _, _ = await sandbox.get_screenshot(sandbox_id)
user_message_for_history = f'{user_input}\n\n'
history.append([user_message_for_history, "Thinking..."])
yield "", history
while True:
# 1. Observe: Get the current screenshot
screenshot_url, _, base64_str = await sandbox.get_screenshot(sandbox_id)
# 2. Think: Prepare messages for the LLM
planner_message = [
HumanMessage(
content=[
{"type": "text", "text": f"This is user's instruction: {user_input}"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {"url": f"data:image/webp;base64,{base64_str}"},
},
]
),
]
system_message = SystemMessage(content=PLANNER_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
history_messages = memory.chat_memory.messages
full_message_list = [system_message] + history_messages + planner_message
# Get LLM response
response_message = await llm.ainvoke(full_message_list)
response = response_message.text()
print("Planner output:", response)
print("---------")
# Update history with the LLM's thought process
match = re.search(r'Action:\s*(.*)', response)
if match:
response = match.group(1).strip()
else:
yield f"Error: No action found", history
history[-1][1] = response # Update the "Thinking..." message
yield "", history
# 3. Grounding
grounding_message = [
HumanMessage(
content=[
{"type": "text", "text": response},
{"type": "text",
"text": f"This is user's screenshot,and the resolution of the screenshot is 1280*720:"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {"url": f"data:image/webp;base64,{base64_str}"},
}
]
)
]
system_message = SystemMessage(content=GROUNDNING_SYSTEM_PROMPT)
full_message_list = [system_message] + grounding_message
response_message = await llm_uitars.ainvoke(full_message_list)
response = response_message.text()
print("Grounding output:", response)
# 4. Act: Parse and execute the action
action_dto = await computer_use.parse_model_output(
dto.ComputerUseParseRequestDto(model="ui-tars",
textContent=response,
))
action = action_dto.actions[0]
await computer_use.execute_computer_use_action(sandbox_id, dto.ComputerUseActionDto(action=action))
# Memory: Store the conversation
memory.chat_memory.add_message(planner_message[0])
memory.chat_memory.add_ai_message(response)
# Check for termination condition
if isinstance(action, dto.FinishedAction):
final_screenshot_url, _, _ = await sandbox.get_screenshot(sandbox_id)
history.append([None, f"Task finished. Final state:\n\n"])
yield "", history
break
await asyncio.sleep(2)
# Prepare for the next loop iteration
history.append([f"Action executed: `{ action.model_dump_json() }`\n\nTaking new screenshot...", "Thinking..."])
yield "", history
except Exception as e:
import traceback
yield f"Error: {str(e)}\n{traceback.format_exc()}", history
with gr.Blocks() as iface:
gr.Markdown("# Playground with LangChain & Gradio")
gr.Markdown("Interact with the Gemini model and maintain conversation history.")
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(render_markdown=True, sanitize_html=False)
user_input = gr.Textbox(placeholder="Enter your task for the agent...")
submit_button = gr.Button("Run Agent")
# Use a generator for the click event
submit_button.click(
fn=playground,
inputs=[user_input, chatbot],
outputs=[user_input, chatbot],
)
user_input.submit(
fn=playground,
inputs=[user_input, chatbot],
outputs=[user_input, chatbot],
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
iface.launch()结果
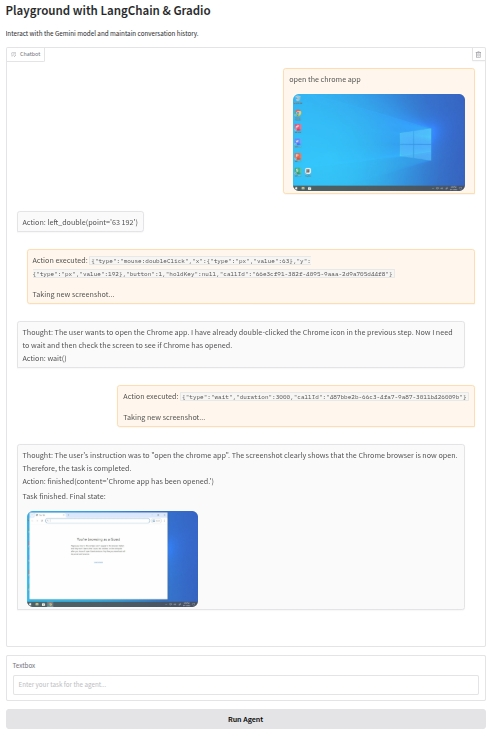
到此为止,您已经成功构建了一个能够理解并在计算机上执行复杂任务的图形用户界面 (GUI) 智能体。 您可以根据需要进一步扩展和优化此智能体,例如添加更多的错误处理、改进用户界面,或集成其他模型和工具,以增强其功能和性能。 祝您在构建智能智能体的旅程中取得成功!